
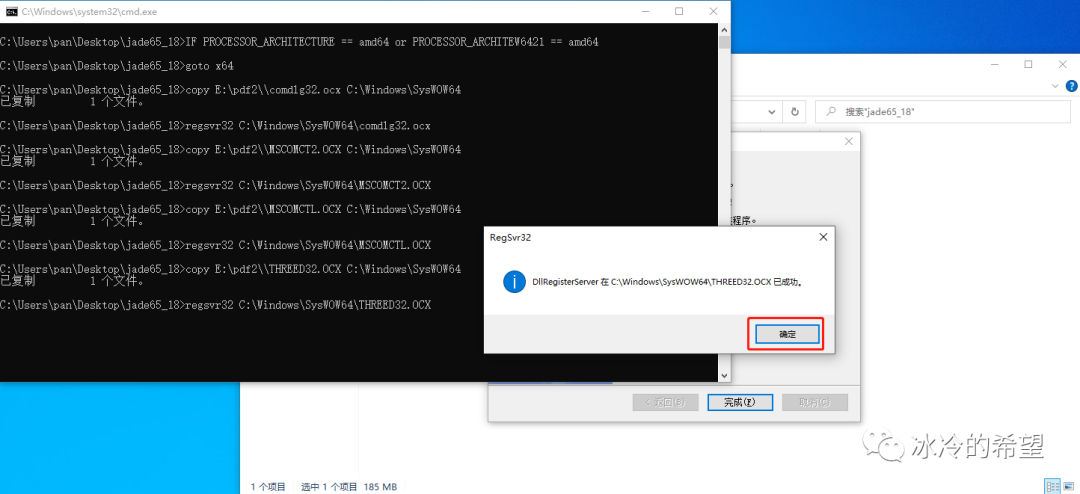
The ARL EQUINOX 3000 - an entry-level full-scale laboratory instrument - uses a 3 kW generator, which powers a long, fine focus X-Ray tube that is connected to both focal or parabolic mirror optics or a Ge (111) monochromator, which offers Kα radiation with the highest flux or brilliant Kα1 radiation, which is ideal for the high resolution. Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers About the ARL EQUINOX 3000 The Thermo Scientific™ ARL™ EQUINOX 3000 instrument can measure the low angles that are needed for this type of investigation, and it eliminates the need for preparations the standard setup allows low-angle measurements to be performed easily (Figure 1). Measurements are needed at very low (<1° 2θ) diffraction angles, which is facilitated by the Thermo Scientific™ ARL™ EQUINOX 3000. The direct measurement of structural arrangement and pore size is made possible by utilizing X-Ray diffraction (XRD).

Recently, it has been hypothesized by various studies that such materials could even be used as a system support material in drug delivery. The pores range from 2 to 6.5 nm and MCM-41 has been applied within catalyst applications as an adsorbent for the treatment of wastewater for chemical reactions. Two of the most widely used mesoporous materials made from silica are MCM-41 and MCM-48.
Image Credit: Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers Within energy storage devices, mesoporous carbon has found wide application, and, in contrast to zeolites, the pores are larger in mesoporous carbon, which means that both the pore size and their distribution can be easily adjusted.įigure 1. ARL EQUINOX 3000 X-ray diffractometer. Though the most widely used material is mesoporous carbon, these types of materials have also found application as catalysts or catalyst supports. Sponsored by Thermo Fisher Scientific - Elemental Analyzers and Phase Analyzers Reviewed by Olivia FrostĪ class of materials with pore sizes ranging from 2 to 50 nm, mesoporous materials are formed by a matrix that is typically created with amorphous silica, alumina, or transition metal oxides.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
